Table of contents
Brushtail Administrator's Guide
MySQL on Linux
This is intended as a primer only, MySQL has extensive documentation. Should work with SUSE, Redhat and Mandrake Linux.
Configuring MySQL
1) create intranet database
2) create intranet user
3) Load brushtail.sql file to populate database tables
4) set root password
Command Line
Start MySQL service with the command
service mysql start
Create MySQL intranet database.
/usr/bin/mysqladmin create intranet
Create intranet user with relevant privileges.
/usr/bin/mysql
mysql > grant select, delete, update, insert,lock tables on intranet.* to user@localhost identified by 'userpassword' ;
mysql > quit
Load sql file
/usr/bin/mysql intranet < mysql_3.3.sql
You change the directory path to mysql_3.3.sql
Set root password.
/usr/bin/mysqladmin -u root password g0dzilla
Mysql administrator
You could administor a linux MySQL installation from a windows PC using the MySQL
administrator utility. Look at the "MYSQL on Windows" page
for more information about MySQL Administrator.
The linux firewall would need to allow incoming connections on tcp port 3306
The root MySQL user needs permissions to be allowed to connect remotely.
- Create remote access using the command line
grant select, delete, update,lock tables, insert on intranet.* to root@'%'
identified by 'rootpassword' ;
or this would specify the pc which is allowed access
grant select, delete, update,lock tables, insert on intranet.* to root@192.168.50.40
identified by 'rootpassword' ;
- Create remote access using Webmin
To do so using Webmin, a web based linux
adminstration utility, would look like this.
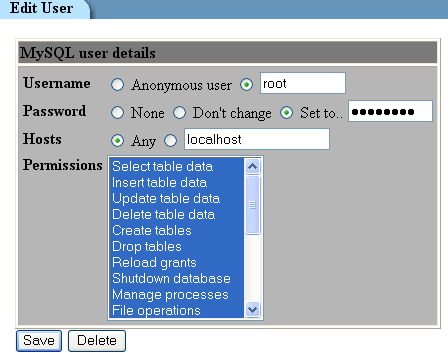
Now download from www.mysql.com, then install, the MySQL Administrator utility
on the remote machine. This provides a nice graphical interface for administrating
MySQL. Then connect to MySQL using new root password.
Backup
MySQL has a utility called mysqldump. This will export the database into a .sql
text file containing sql statements.
Create a script containing the mysqldump command (check MySQL directory path)
/usr/bin/mysqldump --add-drop-table intranet > backup.sql
-u root -prootpassword
Use Cron to run bakup regularly
Files
Document and image files are not stored inthe database. The uploads
directory will needd to be backed up as well.
Restore Backup
/usr/bin/mysql intranet < backup.sql -u root -prootpassword
Table of contents
